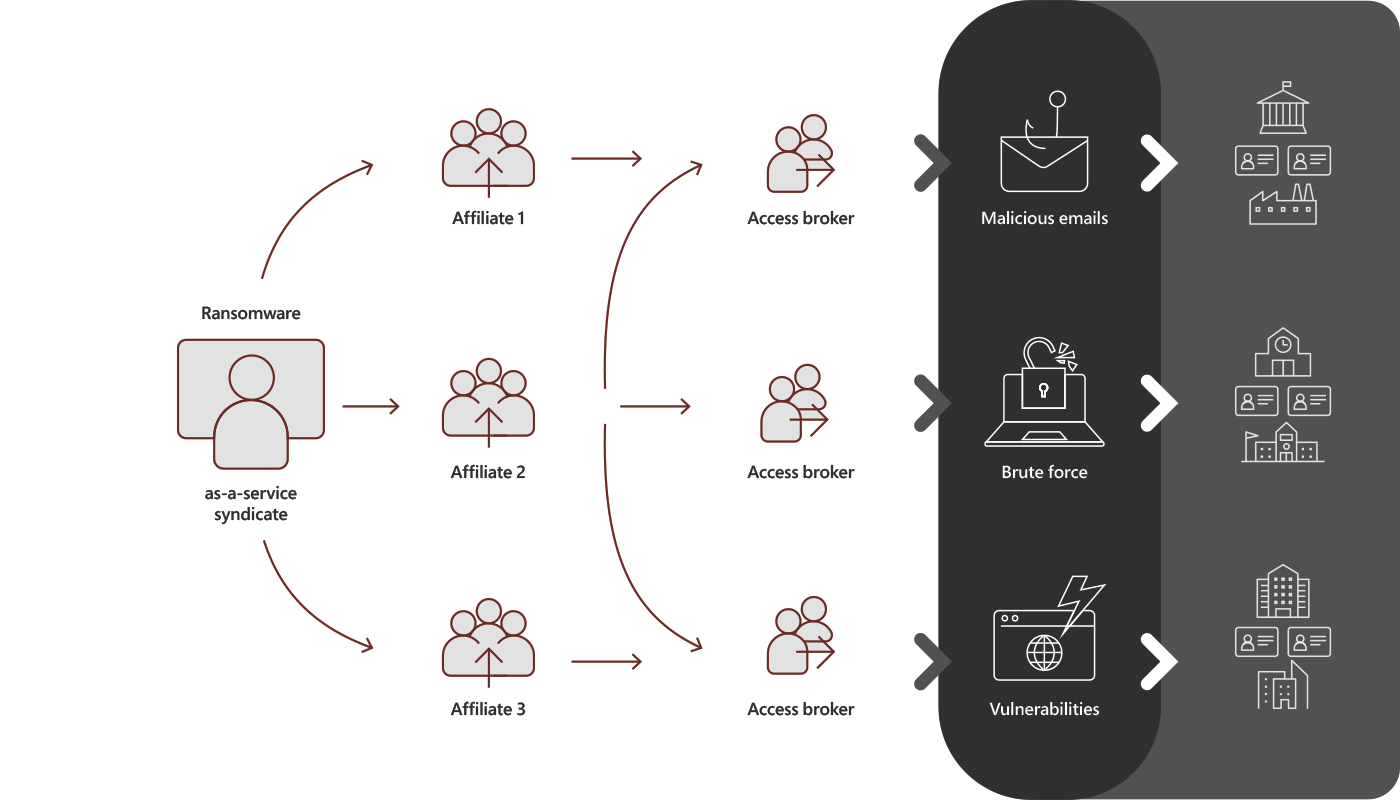
RaaS?
Ransomware as a service is a cybercrime business model where ransomware operators write software and affiliates pay to launch attacks using said software. Affiliates do not need to have technical skills of their own but rely on the technical skills of the operators.
Ransomware as a Service
Recently, a new Ransomware variant has emerged, adding to an already diverse market of Ransomware that includes but is not limited to Lockbit, Bad Rabbit, REvil, WannaCry, Ryuk, and Petra. GhostLocker emerged from the cauldron of GhostSec, a highly organized hacktivist group associated with the international network of hacktivists “Anonymous”. GhostSec officially created a Telegram channel for its new tool, GhostLocker, on October 8, 2023, emerging as another entity that organizations must be vigilant about.

GhostLocker Ransomware
GhostLocker RaaS
GhostSec labelled GhostLocker as the “new generation of RaaS”, boasting of its military-grade encryption on runtime which ensures that victims cannot decrypt the software through decompilation or obtaining the decryption key by inspecting web requests or in the case of a server exposure.
The ransomware is reportedly “fully undetectable,” with the threat actor boasting a zero detection rate for all major antivirus software.
Post its creation, the GhostLocker Telegram channel swiftly amassed over 100 subscribers, gaining traction in GhostSec’s official channel as well. Some users even expressed interest in a demo to further promote the tool, particularly in a business context.
Despite its substantial price tag – initially at $999 during the beta phase and later at $4,999 – the threat actor only requests a 15% commission fee from all revenue after the one-time payment.
GhostSec also offers to manage all negotiations for their affiliates while providing a web panel for monitoring negotiations should affiliates wish to intervene at any point.
The threat actor has also noted that the current version of GhostLocker is an early version and is committed to significant improvements in the future, with plans to reduce its total file size and enhance its encryption speed as the first step.
A page out of LockBit’s Ransom note?
After GhostSec posted a video demonstration showcasing GhostLocker’s functionality, intelligence analysts were quick to note a striking similarity in the ransom note designed by GhostSec to that of LockBit Ransomware.
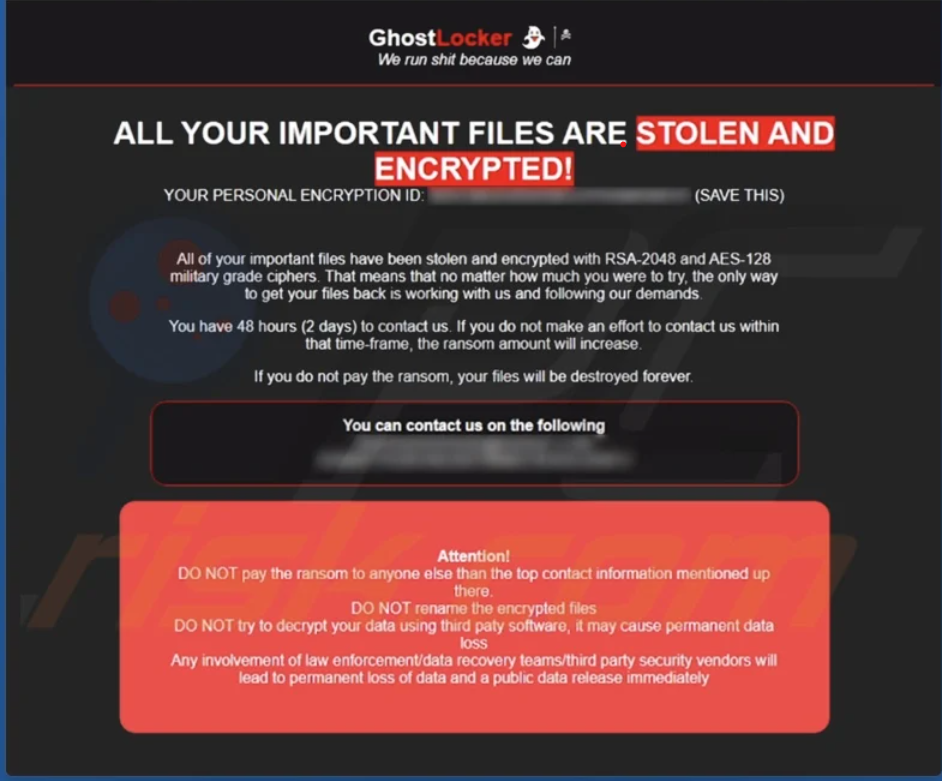
GhostLocker ransom note
LockBit ransom note
Who are GhostSec?
GhostSec is a group associated with the larger hacktivist collective Anonymous. GhostSec emerged as a splinter group in the aftermath of the Charlie Hebdo terrorist attacks in Paris in January 2015. The group claims to focus on counterterrorism efforts and monitoring online activities related to terrorism.
GhostSec’s mission is to identify and report websites, social media accounts, and other online platforms used by extremist and terrorist groups. They gather intelligence on these organizations and individuals with the goal of disrupting their online presence. GhostSec has been involved in uncovering and reporting various websites and social media accounts associated with terrorist organizations. The group is acknowledged for its actions against ISIS-affiliated websites that disseminated Islamic extremism, as part of the campaign recognized as #OpISIS.
In addition to its primary objective, GhostSec has engaged in the promotion of human rights and the defense of online freedom in various countries, most notably Cuba. The group has also participated in the Russia-Ukraine conflict, executing a series of cyberattacks against the Russian government.
It’s important to note that, like other Anonymous-affiliated groups, GhostSec is decentralized, and its members often operate anonymously. They do not have a central leadership structure, and their actions can vary widely. Some view their activities as a form of hacktivism aimed at countering terrorism, while others criticize their methods and question the effectiveness of their efforts.
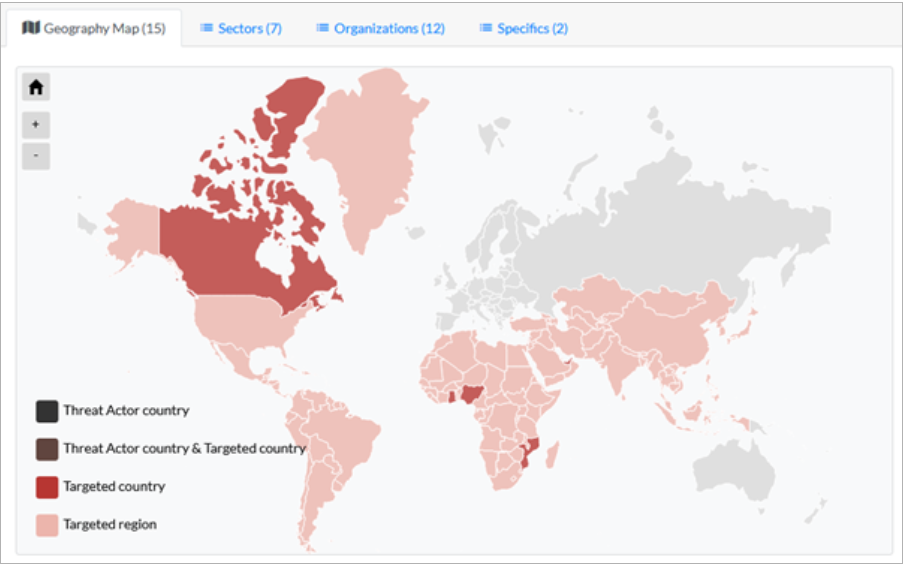
Recent GhostSec Threat Activity Map
